Organizations continue to migrate and adopt AWS Cloud Services and offer digital services to their customers and stakeholders. Service providers especially in compliance focused markets such as healthcare, financial services and public sector markets must adhere to security best practices to ensure the integrity of their information assets. AWS provides a wide range of tools and services to help users implement security best practices. However, many organizations may not have the experience or expertise required related to security and compliance best practices on the AWS cloud. In order to help such organizations, stackArmor has developed a light-weight Security Review Report (SRR) product.
Security Review Report
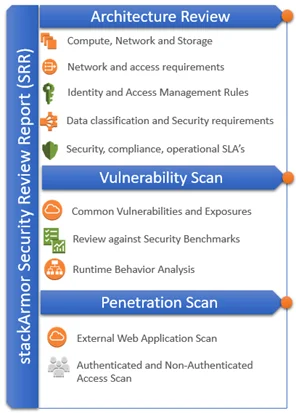
stackArmor has developed the Security Review Report (SRR) artifact as a first step for organizations to assess their risk posture for AWS cloud based workloads and applications. The Security Review Report covers three major technology focused components of a cloud-based environment that includes:
- Review of the architecture of the hosting environment
- An internal vulnerability scan of the hosting environment and finally
- An external penetration scan of the hosting environment.
The infographic shows how a full-stack architecture review typically consists of the environment, application(s), data, operating system and the cloud platform that must be protected. The actual current state of the security state is assessed by reviewing the structure, evaluating the software on the platform and the external exposure and threat surface available for attacks from the outside. The stackArmor Security Review Report (SRR) is a great light-weight starting point for organizations trying to assess their security posture.

Architecture Review
Creating a robust and secure architecture on AWS EC2 requires understanding core principles that ensure that the hosting environment is secure and robust to meet business and security standards for online systems. The architecture review consists of the following key elements:
- Access management and control through means such as VPN, SSH, Bastion host, RDP or similar means to ensure that privileged users such as administrators and developers are securely accessing the environment.
- Segmentation of the various layers of the application including using Application or Elastic Load Balancers (for public facing sites), private sub-nets for web servers, separate security groups and subnets for database servers and services.
- Data protection policies including the use TLS/https for encrypting data in motion including reviewing TLS termination end points. Using AES-256 encryption for data at rest in EBS volumes or S3 buckets. Reviewing database encryption especially of sensitive data fields.
- Continuous Monitoring configuration and setup through the use of cloud-native services such as Amazon CloudWatch, CloudTrail, Config, Macie and external services such as Splunk.
- High-availability and fault tolerance using Multiple-Availability Zones, and architecting for redundancy.
Misconfigurations Scan
AWS cloud services need to be configured to ensure that security best practices are followed. Given that a lot of organizations may not be familiar with some of these best practices, stackArmor performs a scan of the configuration and setup using the EC2 API’s and covers key services to detect potential misconfigurations. The stackArmor ThreatAlert scan reviews the various settings and configurations of AWS components and services. A sample of the services and their misconfigurations are illustrated in the table below.
|
Misconfiguration |
Severity Score | Cloud-specific Sub- category |
| Non-VPC RDS Security Group contains private RFC-1918 CIDR |
8 |
Security Group |
| RDS Security Group network larger than
/24 |
3 |
Security Group |
| RDS Security Group subnet mask is /0 | 10 | Security Group |
| RDS Security Group contains 0.0.0.0/0 | 5 | Security Group |
| ELB is Internet accessible. | 1 | Elastic Load Balancer |
| SSL listener is not using the ELBSecurity Policy-2014-10 policy |
N/A |
Elastic Load Balancer |
| Custom listener policies are discouraged. | 8 | Elastic Load Balancer |
| ELBSecurityPolicy-2011-08 is vulnerable and deprecated |
10 |
Elastic Load Balancer |
| ELBSecurityPolicy-2014-01 is vulnerable to poodle bleed |
10 |
Elastic Load Balancer |
| Unknown reference policy. | 10 | Elastic Load Balancer |
| SSLv2 is enabled | 10 | Elastic Load Balancer |
| SSLv3 is enabled | 10 | Elastic Load Balancer |
| Server Defined Cipher Order is Disabled. |
10 |
Elastic Load Balancer |
| Deprecated Cipher Used. | 10 | Elastic Load Balancer |
Vulnerability Scan
The internal vulnerability scan is performed using tools to help identify presence of vulnerabilities as reported to the NIST’s CVE database by various vendors. Tools such as Amazon Inspector, Tenable Nessus or OpenSCAP are commonly used to detect such vulnerabilities. The findings are grouped into Critical, High, Medium and Low’s. The best practice is to remediate Critical and High. With a plan of action to remediate Medium’s and Low’s. It is very common for such vulnerabilities to show up in the system due to delays in applying patches that typically includes a yum update for Linux systems or a WSUS update for Windows. AWS services such as Amazon EC2 Systems Manager provides a native patching solution that provide a systematic solution.
Penetration Scan
An external penetration scan helps identify vulnerabilities in the exposed web application. Typically, this scan is performed in anonymous mode and authenticated mode. The penetration scan helps detect issues such as SQL injection, XSS, click-jacking and other common web application related vulnerabilities. The penetration scan is typically performed using tools such as Tenable Nessus or Metasploit amongst others.
Prior to beginning any scanning activity, it is important to follow the prescribed protocol and procedures mandated by AWS that includes submitting a request form and getting approvals.